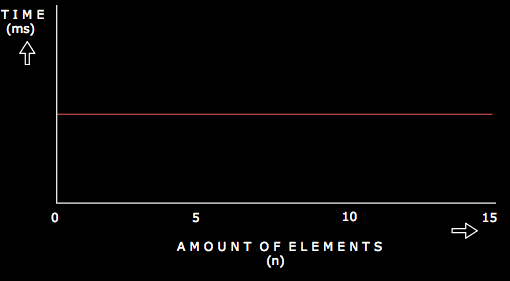Constant Runtime
2020-08-04
Constant runtime O(1) / time complexity is the term used to refer to an algorithm which will always execute in the same amount of time regardless of the amount of data or input fed into it.
Here are a few examples
- Getting the first element of an array
- Popping an item off a stack
- Creating a function that takes no arguments and returns "Hello World"
There is something common among these operations: they do not depend on the size of any data or input and hence, they are constant time or they have a Big O of O(1) .
Let me use the third example to further illustrate. Oh and I'll be using JavaScript for all my code examples but they're fairly straightforward and easy to implement in other languages as well.
function sayHello() {
return "Hello World";
}
With this sayHello function, it will always run in the same amount of time regardless of whatever is passed into it. Let's assume for some funny reason you decide to pass in an array as a parameter. The code will then look something like this.
const numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
function sayHello(array) {
return "Hello World";
}
console.log(sayHello(numbers));
The sayHello function will still run in the same time because it does not make use of the elements in the numbers array for any of its operations. The numbers array could contain as many as 500 elements and it still won't affect how sayHello runs. This is why it as a Big O of O(1).
Let's take another example. Say we have 3 arrays of different length. Let's write a simple program to access the first element of each array.
const array1 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
const array2 = [0, 10];
const array3 = [50,60,70,80,90,100,110,120,130];
console.log(array1[0]);
console.log(array2[0]);
console.log(array3[0]);
For all the three arrays, it takes the same amount of time to access the first element eventhough they are of different sizes. This is why accessing the first element of an array is considered a constant time process.
Below is a graph that shows how a constant time algorithm varies with time
The next topic we'll look at is the Linear runtime or O(n). Until then, Happy Coding! 👊